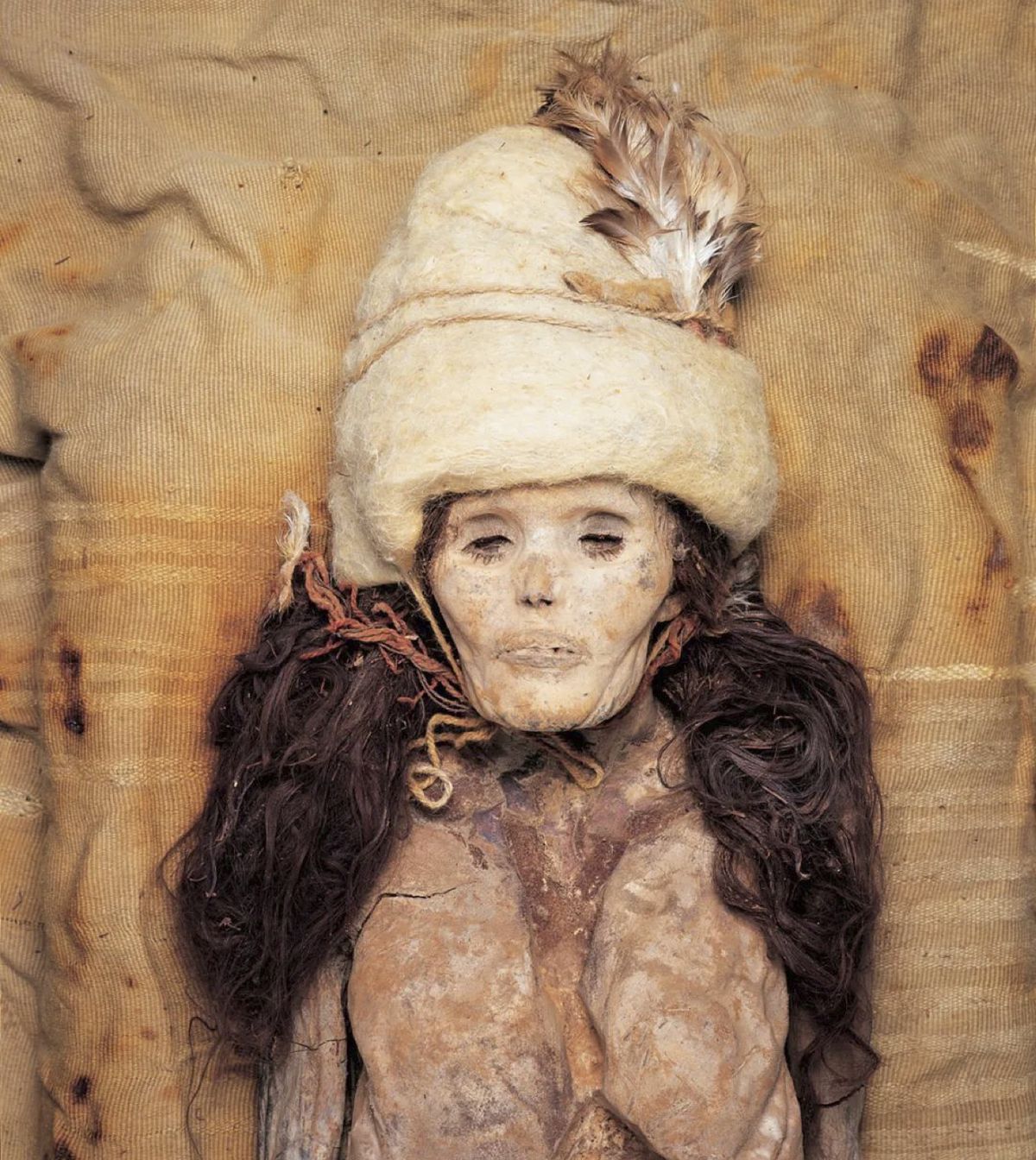
Archaeologists have made an exciting discovery in Egypt, unearthing an ancient city near the historic site of Abydos that dates back over 7,000 years. The city is believed to have been established during Egypt’s Early Dynastic Period, making it one of the oldest cities ever found in Egypt.

Abydos holds great significance in Ancient Egyptian history, as it was considered one of Egypt’s earliest capitals and an important religious center. The burial ground in Abydos contains tombs from the first pharaohs of Egypt, marking it as an influential site.
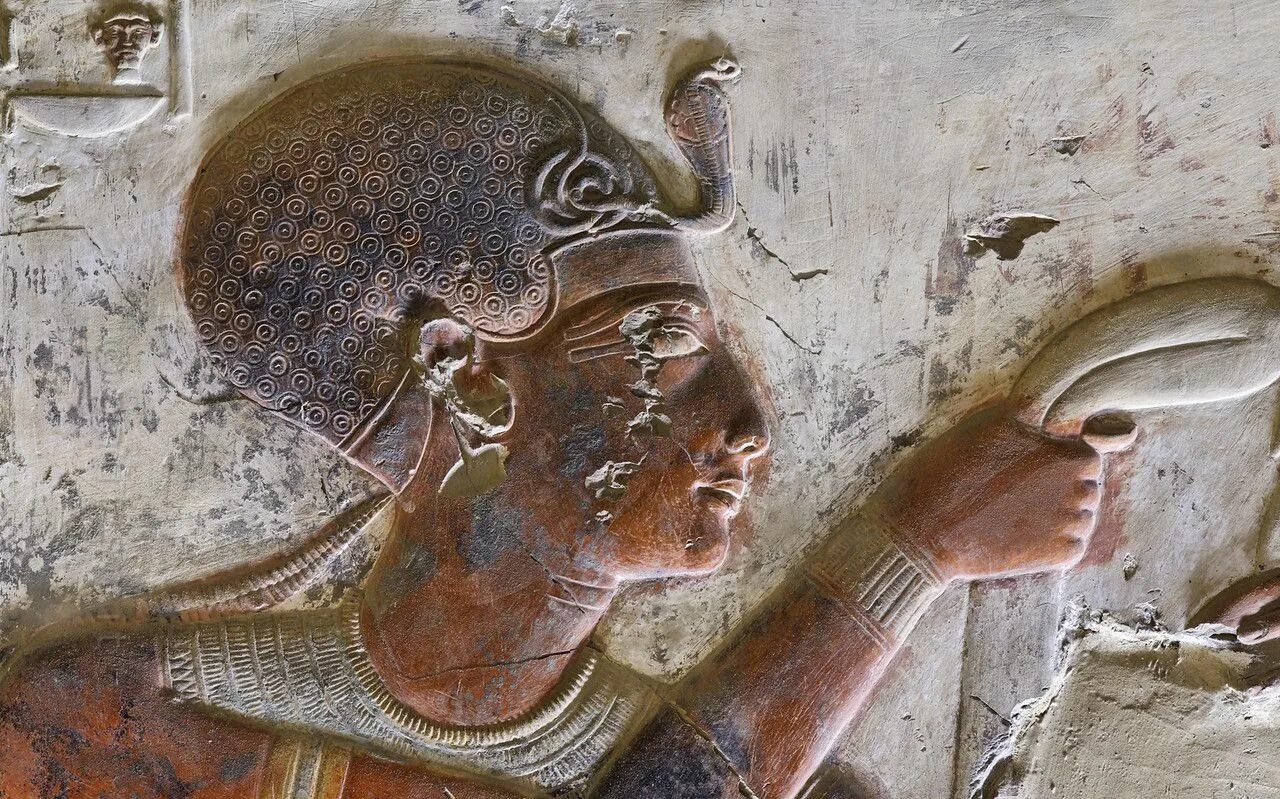

The newly discovered city near Abydos reveals even more about early Egyptian civilization. archaeologists estimate the city was populated from approximately 5,300 BCE to 3,000 BCE. At its peak, it is believed to have had a population of 10,000 – 15,000 inhabitants.

Several features of the long-lost city have been excavated so far. These include the ruins of brick houses, artifacts such as pottery and tools, and a cemetery with graves dating back to 3,000 BCE. One especially notable find is the remains of a 15-foot high mudbrick wall that likely served as a fortification for the city.

The ancient city provides insight into a formative time period in Ancient Egypt when early rulers were unifying the civilization and establishing Egypt’s distinctive culture and traditions. Its proximity to the sacred site of Abydos shows the importance of the area.
Further excavation of the city near Abydos will reveal more details about daily life, trade, architecture, and governance in what was one of the earliest Egyptian cities. The discovery adds to our knowledge of Early Dynastic Egypt while also highlighting Abydos’ key role in the development of early civilization in the region.